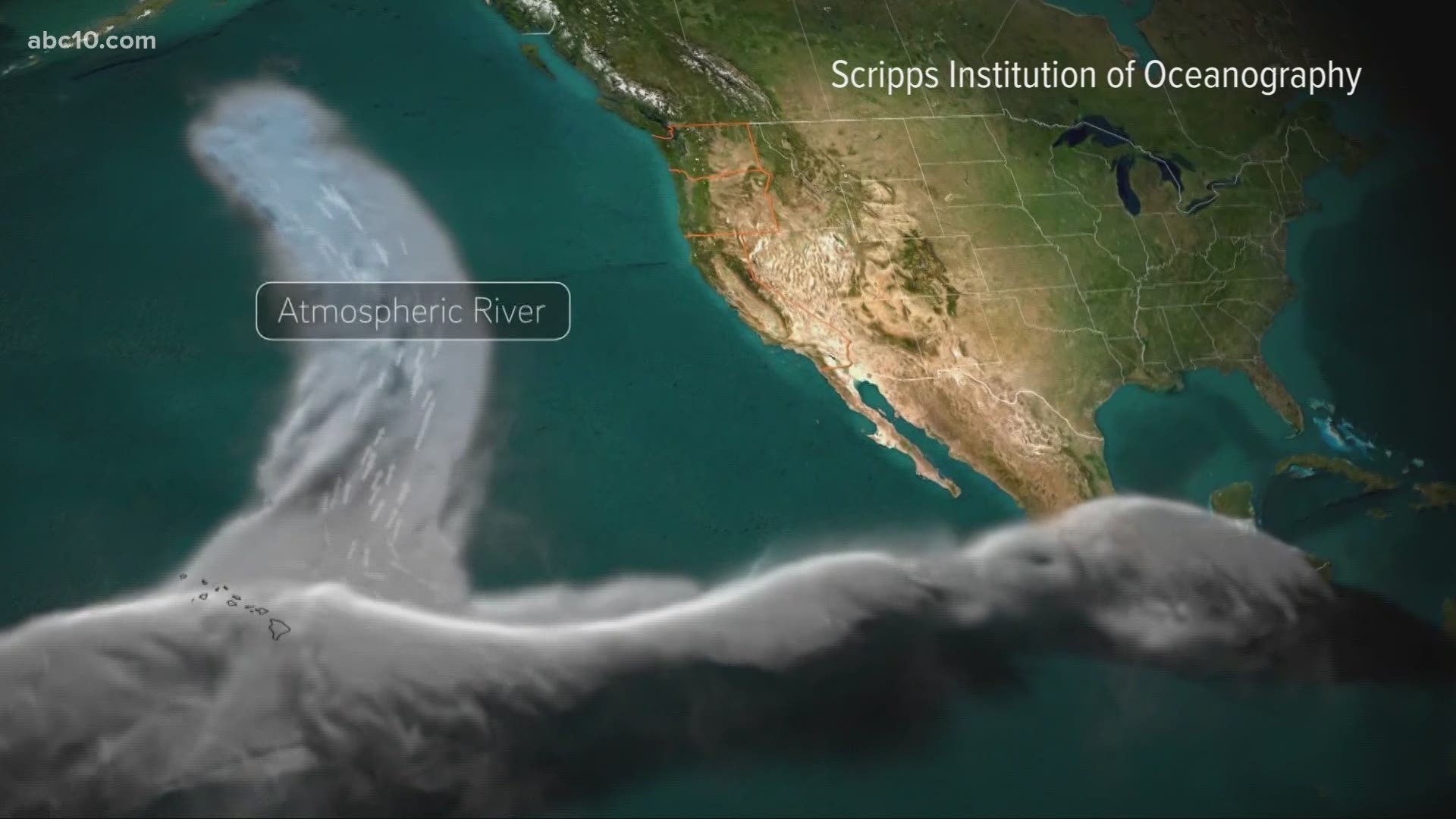
SACRAMENTO, Calif. — California weather is rarely average. Historically, the state has well above or well below average rain and snow. One of the keys to prepare for these wild swings is a better understanding of atmospheric rivers.
The Center for Western Weather and Water Extremes or CW3E is at the heart of this research.
They are studying these large water transport systems in the Pacific. Atmospheric rivers can hold more than twice the water as the Amazon. At times, they can be the most hazardous storms for the West Coast, but they can also be largely beneficial, delivering about 50% of California’s rain and snow. All of it needed for drinking, agriculture and sustaining life in the Golden State.
California has the largest variability in year to year precipitation. Meaning each year can deliver big differences in rain and snow. It's bigger than any other state in the county. And Julie Kalansky, Deputy Director at the CW3E, says climate forecasts are showing those differences are only going to grow in the coming years. Kalansky describes it as a sort of whiplash from wet to dry conditions; dry years get drier and wet years get wetter.
Understanding how to better manage these wild swings is a primary focus for water managers. If a big storm is taking aim at the state, they can release water to make room in reservoirs to prevent flooding. During drier times when these storms head farther north, they can slow down water releases.
Watch the ABC10 weather team's research on atmospheric rivers
How atmospheric rivers are becoming more dangerous due to climate change:
Researchers say that atmospheric rivers are becoming worse due to climate change and could cause more flooding and mudslides as more rain hits rather than snow.
From droughts to flooding, here's how California is trying to better understand atmospheric rivers:
California weather is rarely average. One of the keys to prepare for these wild swings is understanding atmospheric rivers.
WATCH ALSO:
Some of the biggest storms to hit the West Coast are called Atmospheric Rivers (AR). They can cause devastating floods and landslides. The lack of ARs can also mean big droughts.