SACRAMENTO, Calif. —
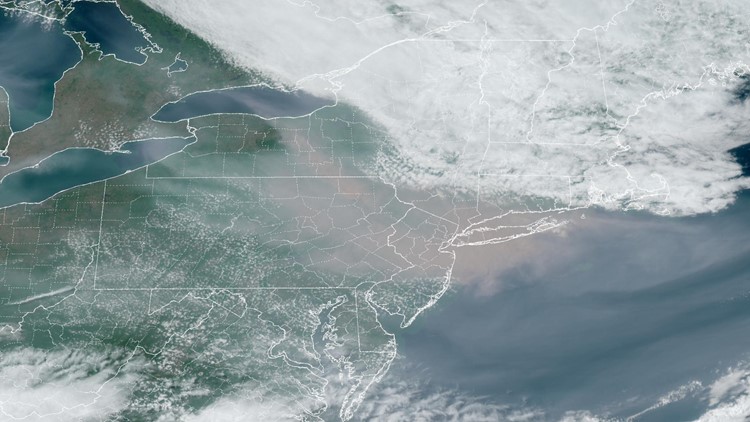
The eastern United States and Canada are experiencing what feels like a summer and fall tradition in the Western U.S. — hazardous air quality thanks to wildfire smoke.
Smoke from a wildfire outbreak in Eastern Canada, sparked by lightning, is currently pushing into some of the most densely populated areas of the United States and Canada.
As of midday Wednesday, New York City topped the list of major cities with the worst air quality in the world. Anything over 300 AQI (Air Quality Index) is considered hazardous, and the AQI in the city at 12 p.m. PDT read 342.
Meanwhile, the air quality in Sacramento and the rest of Northern California remains near perfect with AQI values in the single digits and teens.
In part due to climate change and a history of poor forest management practices, the past decade has featured the deadliest, largest and most destructive wildfires in recorded history in California. Although fire season is year-round, it peaks in the late summer and fall in California and the same period often features hazardous AQI readings due to the smoke produced by the fires.
Although the wet winter has provided hope for a below average fire season, at least for high elevations, the state is certain to be affected by wildfire and bad air quality days as the year continues.
How is Air Quality Measured?
The Air Quality Index is a measure of how five air pollutants, including particulate matter (PM2.5), ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide contribute to how healthy or unhealthy the air is.

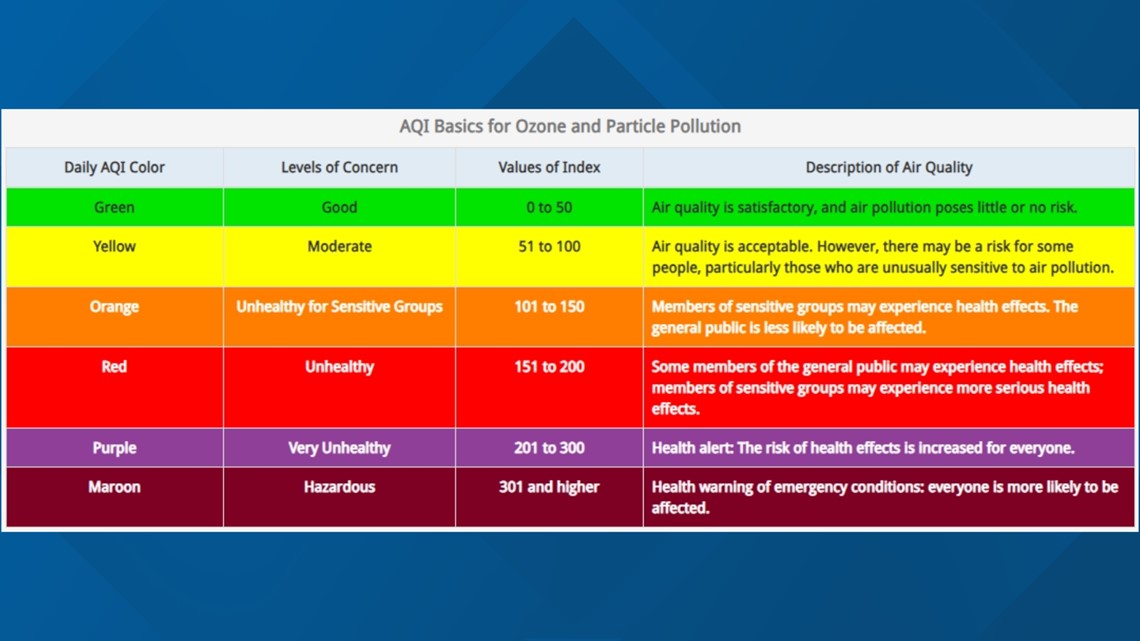
"Think of the AQI as a yardstick that runs from 0 to 500. The higher the AQI value, the greater the level of air pollution and the greater the health concern," according to the website Air Now, "For example, an AQI value of 50 or below represents good air quality, while an AQI value over 300 represents hazardous air quality."
This map by Purple Air gives up to the minute air quality readings across the world.





















